You may already know Docker images can be signed. Today we would discuss a way to automate images signature, using OpenShift.
Lately, I stumbled upon a bunch of interesting repositories:
https://github.com/redhat-cop/openshift-image-signing-scanning: ansible playbook configuring an OCP cluster, building a base image, setting up a service account and installing a few templates providing with docker images scanning and signing
https://github.com/redhat-cop/image-scanning-signing-service: an optional OpenShift third-party service implementing support for ImageSigningRequest and ImageScanningRequest objects
https://github.com/redhat-cop/openshift-event-controller: sources building an event controller that would watch for new images pushed to OpenShift docker registry
Although these are amazing, I could not deploy them to my OpenShift Origin, due to missing subscriptions and packages.
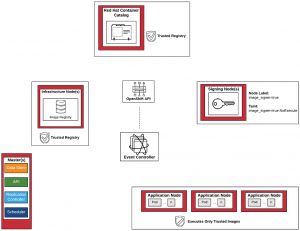
image signing environment overview
In an effort to introduce CentOS support, I forked the first repository from our previous list, and started rewriting what I needed:
https://github.com/faust64/openshift-image-signing-scanning
A typical deployment would involve:
Generating a GPG keypair on some server (not necessarily related to OpenShift)
Depending on your usecase, we could then want to configure docker to prevent unsigned images from being run on our main OpenShift hosts
Next, we would setup labels and taints identifying the nodes we trust signing images, as well as apply and install a few templates and a base image
At which point, you could either install the event-controller Deployment to watch for all your OpenShift internal registry’s images.
Or, you could integrate images scanning and signature yourself using the few templates installed, as shown in a sample Jenkinsfile.
